
|
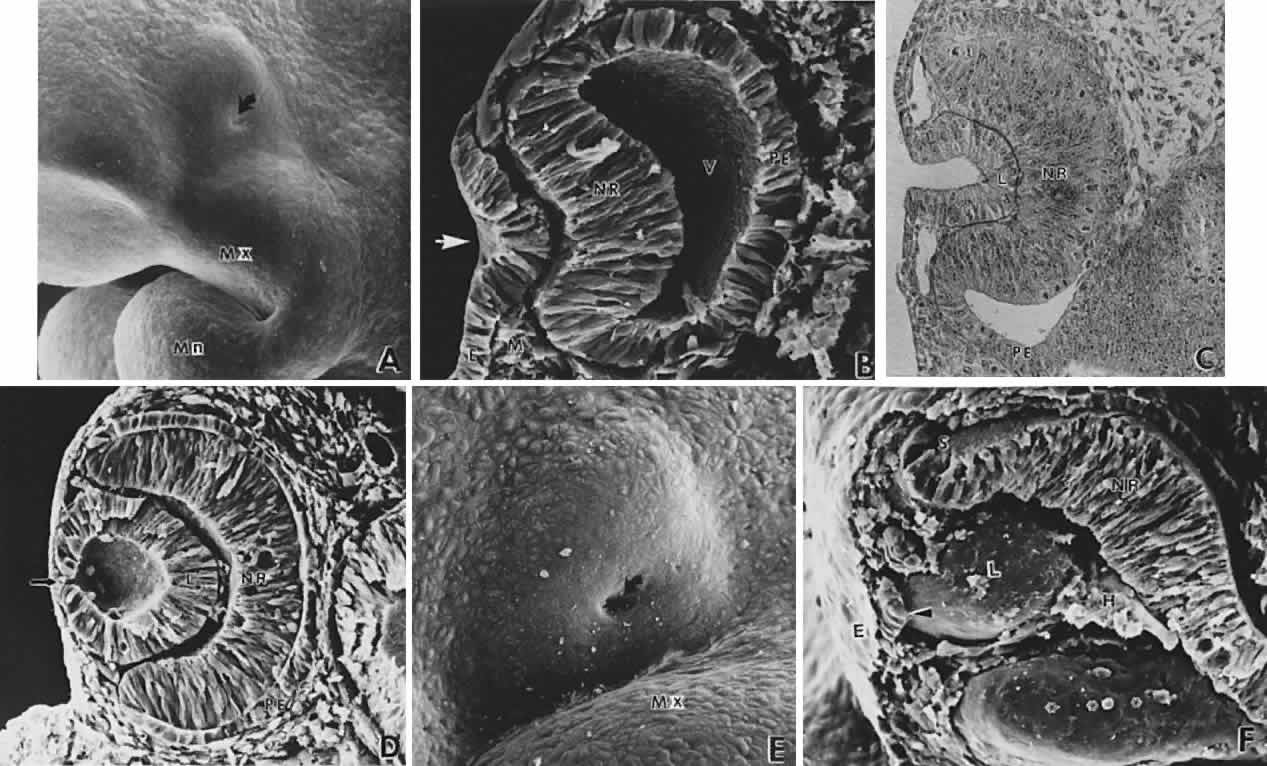
| Fig. 9. Invagination of the optic cup and lens vesicle. Mouse embryos are illustrated. A. Embryo of somite pairs (fifth week in a human). On external examination, the invaginating lens placode can be seen (arrow). Note its position relative to the maxillary (Mx) and mandibular (Mn) prominences of the first visceral arch (× 106). B. Embryo of the same age as in Figure 3A. Frontal fracture through the lens placode (arrow) illustrates the associated thickening of the surface ectoderm (E). Mesenchyme (M) of neural crest origin is present adjacent to the lens placode. Distal portion of the optic vesicle thickens concurrently, as the precursor of the neural retina (NR), whereas the proximal optic vesicle becomes a shorter, cuboidal layer that is the anlage of the retinal pigmented epithelium (PE). The cavity of the optic vesicle (V) becomes progressively smaller (× 367). C. Epithelium of the lens placode continues to invaginate (L). There is an abrupt transition between the thicker epithelium of the placode and the adjacent surface ectoderm, which is not unlike the transition between the future neural retina (NR) and the future pigmented epithelium (PE). (Periodic acid-Schiff's stain; × 443) D. As the lens vesicle enlarges during the eleventh day, the external opening, or lens pore (arrow), becomes progressively smaller. The lens epithelial cells at the posterior pole of the lens elongate to form the primary lens fibers (L). NR, anlage of the neural retina; PE, the anlage of the pigmented epithelium (now a very short cuboidal layer) (× 300). E. External view of the lens pore (arrow) and its relationship to the maxillary prominence (Mx)—32 somite pairs (× 260). F. Frontal fracture reveals the optic fissure (*) where the two sides of the invaginating optic cup meet. This forms an opening in the cup allowing access to the hyaloid artery (H), which ramifies around the invaginating lens vesicle (L). The former cavity of the optic vesicle is obliterated except in the marginal sinus (S), at the transition between the neural retina (NR) and the pigmented epithelium. E, surface ectoderm (× 307). |