

|
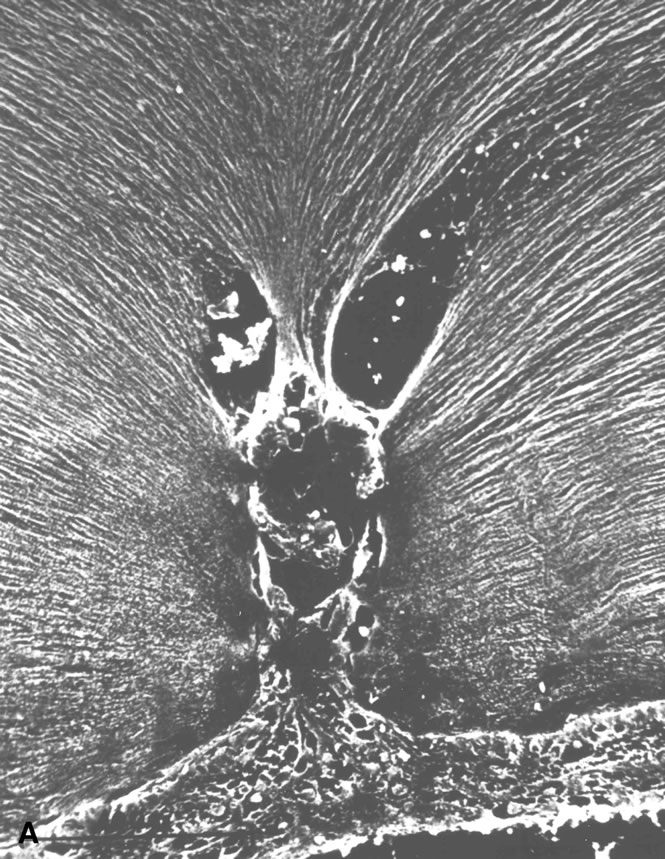
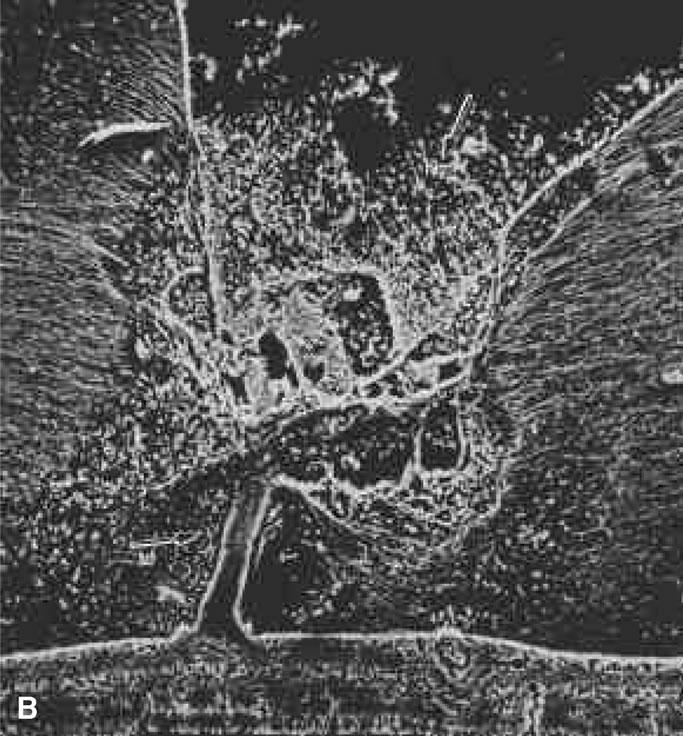
| Fig. 10. A. Cystic retinal tuft. The tuft is a cystoid formation of fibers, similar to those of the nerve fiber layer, and cells similar to those found in the inner plexiform layer of the retina. The tuft is connected to the internal limiting lamina of the retina. This scanning electron micrograph shows the insertion of the vitreous collagen fibers on the tuft's apical surface. Their orientation changes toward the tuft's surface. B. Verruca. The verruca has a structure similar to that of a tree. Its “roots” are embedded in the inner layers of the retina. Cellular elements resembling cells of the inner plexiform layer can be seen near the retinal surface. The “trunk” of this structure extends from the retina to the middle parts of the vitreous cortex. The “branches” of the verruca are intertwined with interrupted vitreous collagen fibers. Local condensation of collagen fibers exists as well as local collagen destruction (arrows) and interruption of the internal limiting lamina of the retina. (Photographs courtesy of Dr. Stephan Dunker.153) |