
|
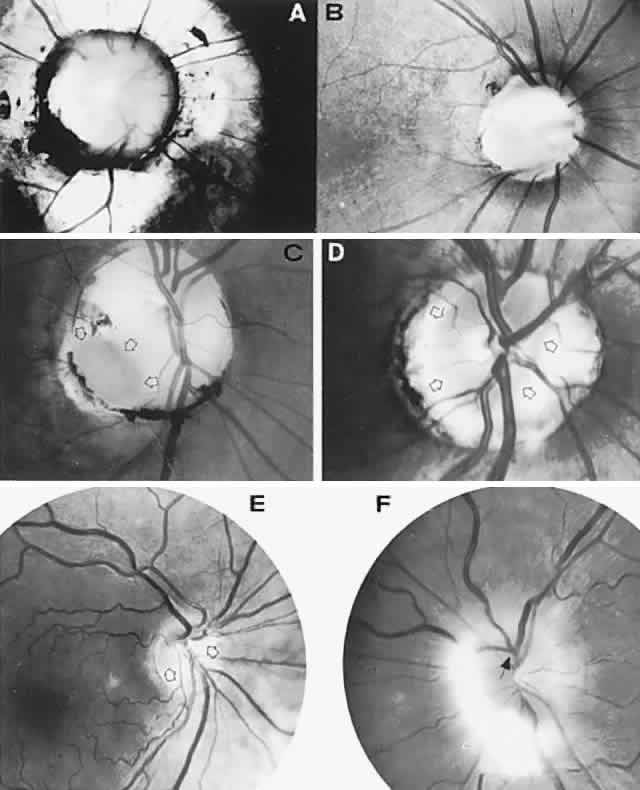
| Fig. 14. Congenital anomalies of the optic disc. A. Large disc coloboma is surrounded by staphylomatous sclera. The disc is partially filled with dysplastic glial tissue. The patient had a transsphenoidal encephalocele that presented as a nasopharyngeal mass. B. Moderate-sized disc coloboma with a central cavity. C. Typical optic pit (arrows) in the inferotemporal aspect of an enlarged disc. D. Unilateral anomalous disc. Nerve substance (outlined by arrows) is truncated nasally and surrounded by a scleral ring. The patient complained of transient visual loss lasting minutes. Vision was 20/20 (6/6) with a mild superotemporal field defect (see also Fig. 15). E. Inferior crescent (Fuchs' coloboma; tilted disc). The actual disc substance (arrows) is hypoplastic, with a large inferonasal scleral crescent. Note hypopigmentation in the inferonasal retinal pigment epithelium and choroid (see field defect in Fig. 16) and anomalous trifurcation of the inferior retinal artery. F. Myelinated nerve fibers on an anomalously elevated disc with no central cup. Note anomalous venous trifurcation (arrow) (see Color Plate 5-1A). |