
|
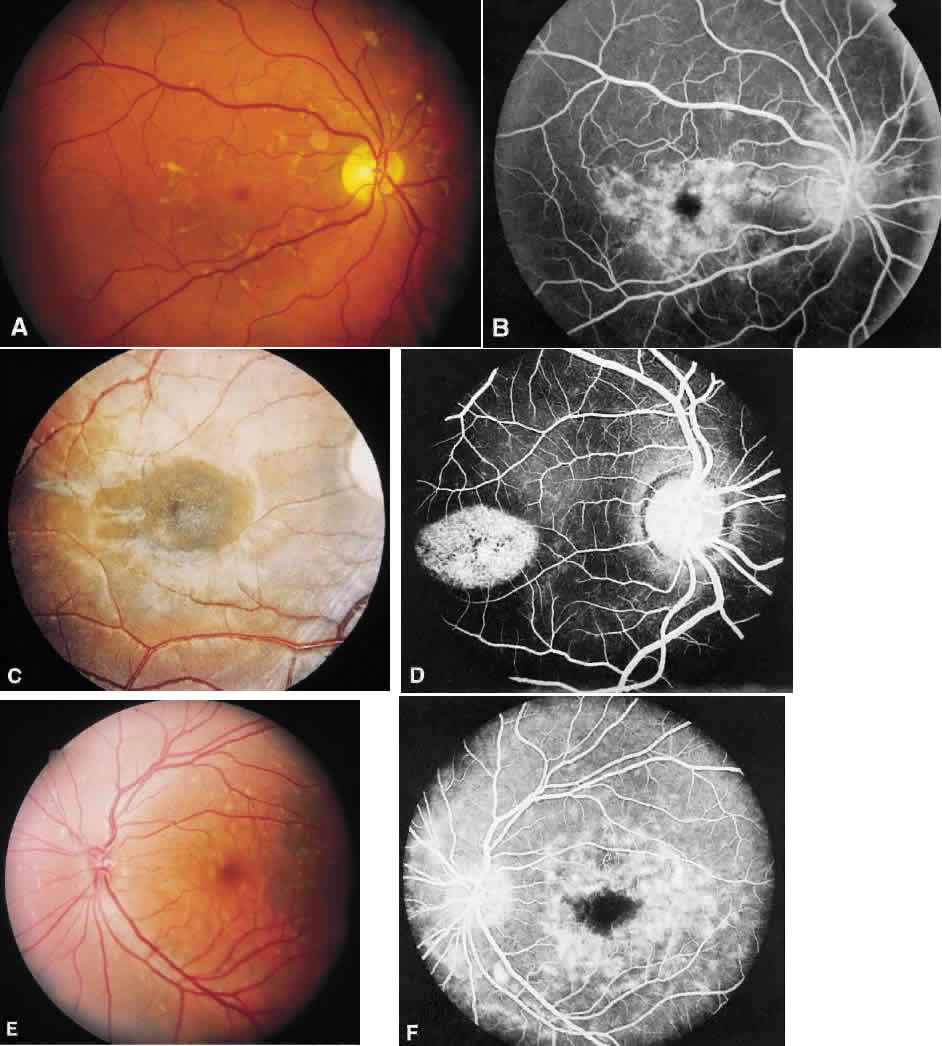
| Fig. 1. Stargardt's disease-fundus flavimaculatus. A. The typical characteristic fundus appearance is a mild macular pigment granularity surrounded by yellowish white flecks. B. On the fluorescein angiogram, these flecks show hyperfluorescence or hypofluorescence, and the background choroidal fluorescence is normal. C and D. A 13-year-old boy had a mild pigment granularity without flecks in both eyes associated with 20/200 vision. Although the granularity appears mild, the fluorescein angiogram shows a large central area of transmitted hyperfluorescence. The silent, dark choroid is evident here. The background choroidal fluorescence is markedly diminished and permits visualization of the retinal capillaries. E and F. A 36-year-old man was asymptomatic with 20/20 vision in each eye. The entire posterior pole and area nasal to the disc show irregularly shaped yellowish white flecks. A fluorescein angiogram shows areas of transmitted hyperfluorescence, many of which do not correspond to the flecks. Despite the widespread flecks, the background choroidal fluorescence is normal. |