
|
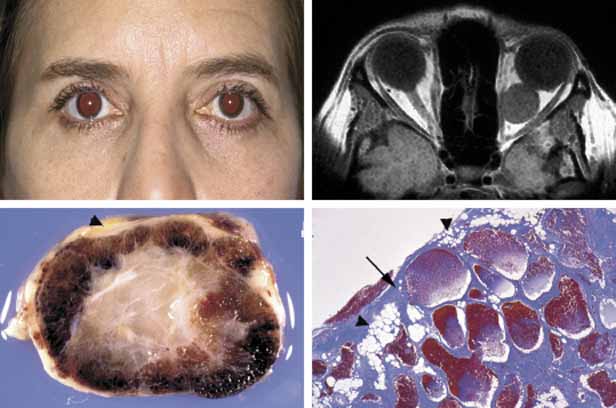
| Fig. 18 Cavernous hemangioma. Despite the presence of a large intraconal tumor in T1-weighted axial MRI, the left globe shows minimal proptosis because of the slowly growing nature of the tumor. This tumor was compressing onto the optic nerve to cause significant papilledema but the patient did not have any extraocular motility disturbance. The gross photograph of the transverse section of the well encapsulated cavernous hemangioma shows multiple loculations of the tumor. Histopathologically the Masson trichome stain demonstrates numerous caverns surrounded by thin fibrous septal, containing clusters of red blood cells. The arrow points to the capsule of the neoplasm. Note that some of the orbital fat is in fact within the fibrous tissues of the tumor (arrowheads). |