|
Fig. 27.
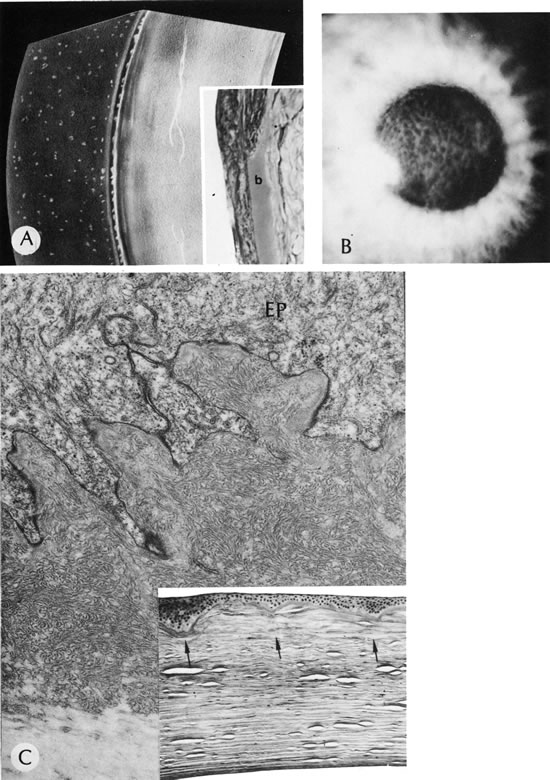
Reis-Bucklers'dystrophy (corneal dystrophy of Bowman type II [CDB-II]). A. Early stage shows small, white dots in continuity with the band of relucency representing Bowman's membrane. Biopsy (inset) is oriented to correspond to drawing. Bowman's membrane (b) is destroyed at the top. B. Moderately advanced stage shows confluence of the whitish subepithelial mounds in the characteristic honeycombed pattern. C. The abundant subepithelial tissue composed of peculiar curly filaments is highly characteristic of the entity. The filaments are closely interwoven, with regions of thin basement membrane. Hemidesmosomes along the epithelial basal cell (EP) are fewer than normal. The basilar cell processes are abnormal. Inset shows degeneration of Bowman's membrane in several foci (arrows indicate membrane remnants). The thick, avascular, fibrous membrane present under the epithelium forms mounds that produce a typical honeycombed pattern in three dimensions. (Courtesy of SEI Photoarchives.) (A modified from Griffith DG, Fine BS: Light and electron microscopic observations in a superficial corneal dystrophy: Probable early Reis-Buckler's type. Am J Ophthalmol 63:1659, 1967; B and C modified from Perry HD, Fine BS, Caldwell DR: Reis-Buckler's dystrophy: A study of eight cases. Arch Ophthalmol 97:664, 1979.)
|