
|
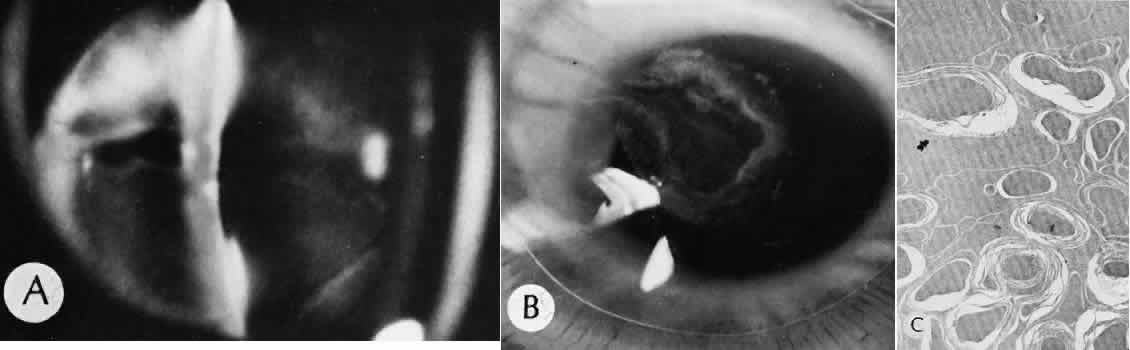
| Fig. 89. Microwave cataract. A. Exposure to microwave energy has produced a posterior cortical cataract in this animal model. B. View of the posterior surface of the crystalline lens at gross dissection. There is a ring of opacity in the region of the application of microwave energy. C. Transmission electron micrograph. The histologic features include lens cells degenerated into globules and surrounded by lamellar material at the edge of the cataract. Relatively normal cortical cells persist at the margin of the injury. (× 12,000.) (Hirsh SE, Appleton B, Fine BS, Brown PV: Effects of microwave radiations to the albino rabbit eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1997;16:315–319.) |