
|
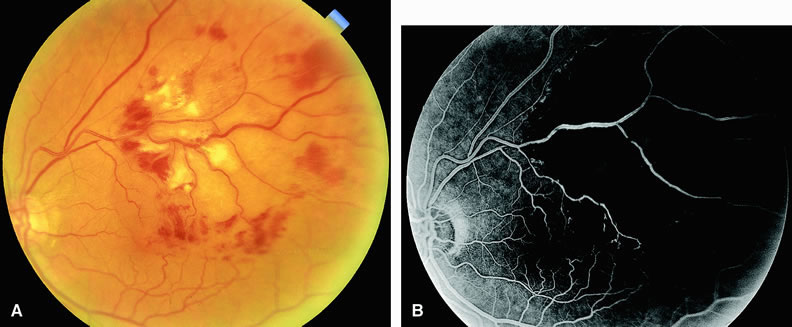
| Fig. 13. A. Fundus of a patient with a branch retinal vein occlusion. Note the presence of dot-and-blot hemorrhages and cotton-wool spots confined to the distribution of the superotemporal retinal vein. The vein itself appears dilated and mildly tortuous. Hemorrhage, cotton-wool spots, and retinal edema extend into the macula. The site of occlusion is at the crossing of the artery and vein (AV crossing). B. Fluorescein angiogram of A reveals a dilated, tortuous supertemporal retinal vein with areas of venous nonperfusion distal to the site of occlusion at the AV crossing. There are regions of hypofluorescence of the choroid resulting from the intraretinal hemorrhage and significant retinal capillary ischemia. |