
|
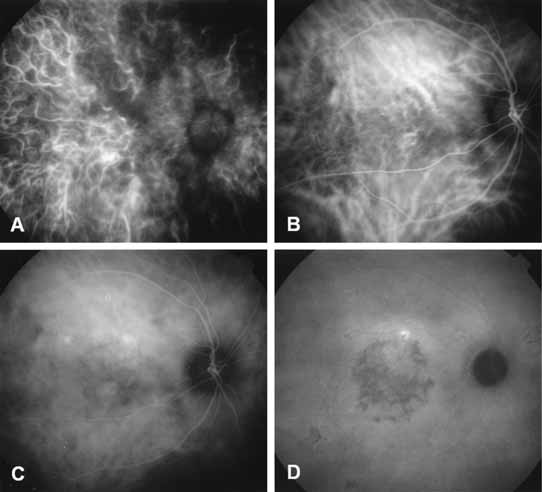
| Fig. 6 Representative phases of indocyanine green (ICG) angiographic study. A, Early filling of the choroidal arterial circulation. A band of hypofluorescence represents a watershed zone between the distribution of the posterior ciliary arteries. The choroidal arterial circulation has filled earlier than the retinal arterial circulation. B, Choroidal venous filling phase of the ICG study. Note the different pattern and distribution of the choroidal veins as opposed to the arteries noted in A. The retinal arterial and venous circulations are now filled. C, Mid-phase ICG angiogram demonstrates fading of the fluorescence of the larger choroidal vessels, as well as retinal vessel. D, Late-phase ICG angiogram is identified by the dark or hypofluorescent optic nerve and the shadowing of the larger choroidal vessels against the background of diffuse fluorescence caused by extravasation of ICG molecules into extravascular space within the choroid. The focal hyperfluorescence represents a focal leakage in a patient with chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. There is also diffuse decompensation of the retinal pigment epithelium and pigmentation in the central macula blocking the background fluorescence. |