
|
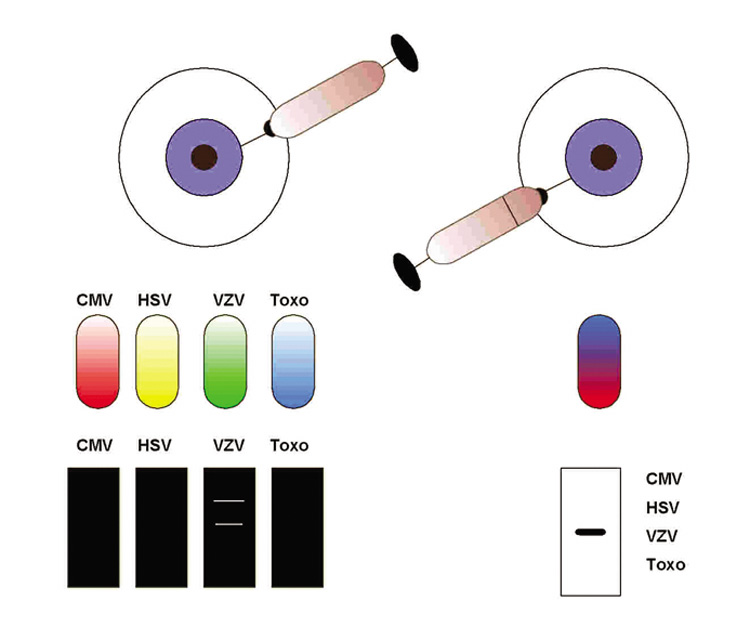
| Fig. 4. Concept for multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Rather than running multiple separate PCR reactions for organisms on a differential diagnosis (such as herpes simplex virus [HSV], varicella zoster virus [VZV], toxoplasmosis [TOXO], and cytomegalovirus [CMV] as shown here), a single reaction is performed with primers for all organisms present. After amplification, a second detection method—either nested PCR or hybridization—is used to perform definitive detection. While sensitivity is marginally reduced in multiplex reactions, numerous organisms can be screened from a single small sample. |