
|
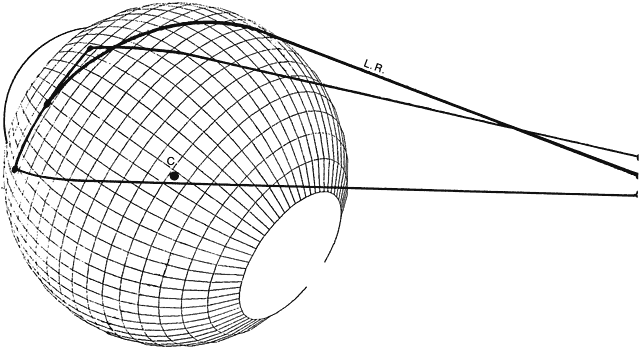
| Fig. 14. Schematic diagram showing lateral rectus muscle path when eye is turned, at 30 degree adduction and 30 degree elevation. Line L.R. is shortest distance (great circle) from center of origin to center of insertion. The path is not taken normally. Upper and lower borders of normal muscle position overlie lateral meridian of eye (C indicates position of eye's center). Abduction continues to be the function of the lateral yaw in all gaze positions. (Volkmann AW: In Helmholtz von H [ed]: Physiological Optics. New York: Dover, 1962.) |