
|
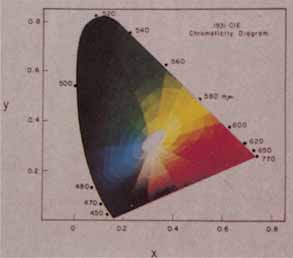
| Fig. 18 CIE chromaticity diagram. The relative amounts of each of the X, Y, and Z primaries in a mixture required to match that color are expressed as chromaticity coordinates (x, y, z). Because the coordinates represent relative amounts of primary [e.g., x = X/(X + Y + Z)], only two of them are required to specify the chromaticity of a color; the luminance quantity is expressed separately as the Y value. Two chromaticity (x, y) coordinates allow this color specification in a two-dimensional space. The z axis is in the plane of the observer. (Adapted from an oil painting by L. Condax; reproduced with permission.) |