
|
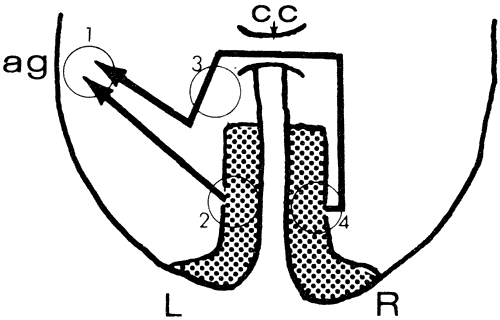
| Fig. 13. Higher integration of vision. Diagram of primary visual cortices (stippled) and their projection to area of angular gyrus (ag) of the left parietal lobe for analysis of visual stimuli. The right calcarine cortex is connected to the left parietal area via a pathway through the splenium of the corpus callosum (cc). Lesion 1 produces alexia and agraphia; lesion 2 produces only right homonymous hemianopia; a combination of 2 and 3 produces right hemianopia and alexia despite intact left hemifields (i.e., the right visual cortex is disconnected from visual analytic areas in the left parietal lobe); lesion 4 produces only left homonymous hemianopia. |