
|
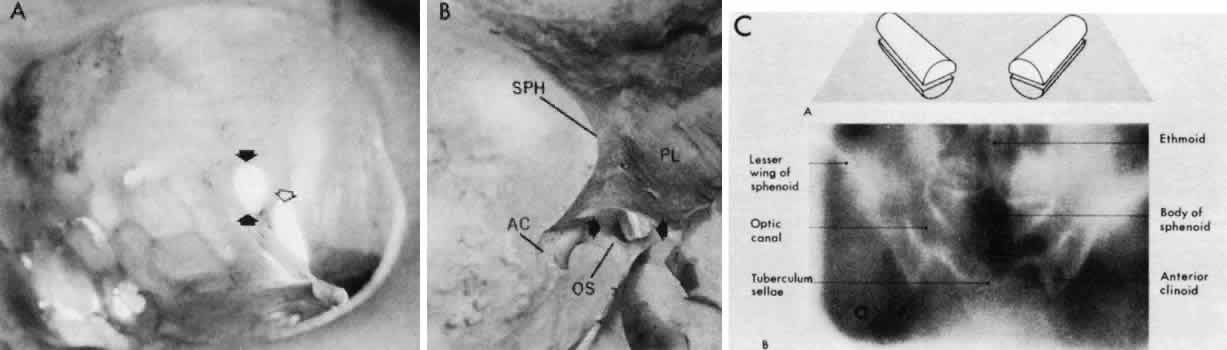
| Fig. 5. The optic canal. A. Anterior view of left orbital apex. Orbital end of optic canal is vertically oval (solid arrows) and separated from the superior orbital fissure (open arrow) by the optic strut. Note transilluminated ethmoidal and sphenoidal air cells that form the medial orbital wall and the medial wall of the optic canal. B. Posterior view of the intracranial aspect of the left optic canal, demonstrating horizontally oval contour. The optic strut (OS) forms the ventrolateral margin of the canal and separates it from the carotid artery. In this preparation, the ethmoidal and sphenoidal air cells have been opened. AC, anterior clinoid; PL, planum; SPH, sphenoidal wing. C. Tomographic section of optic canals in upper diagram. Normal axial tomogram below. (C from Harwood-Nash DC: Optic gliomas and pediatric neuroradiology. Radiol Clin North Am 10:83, 1972) |