
|
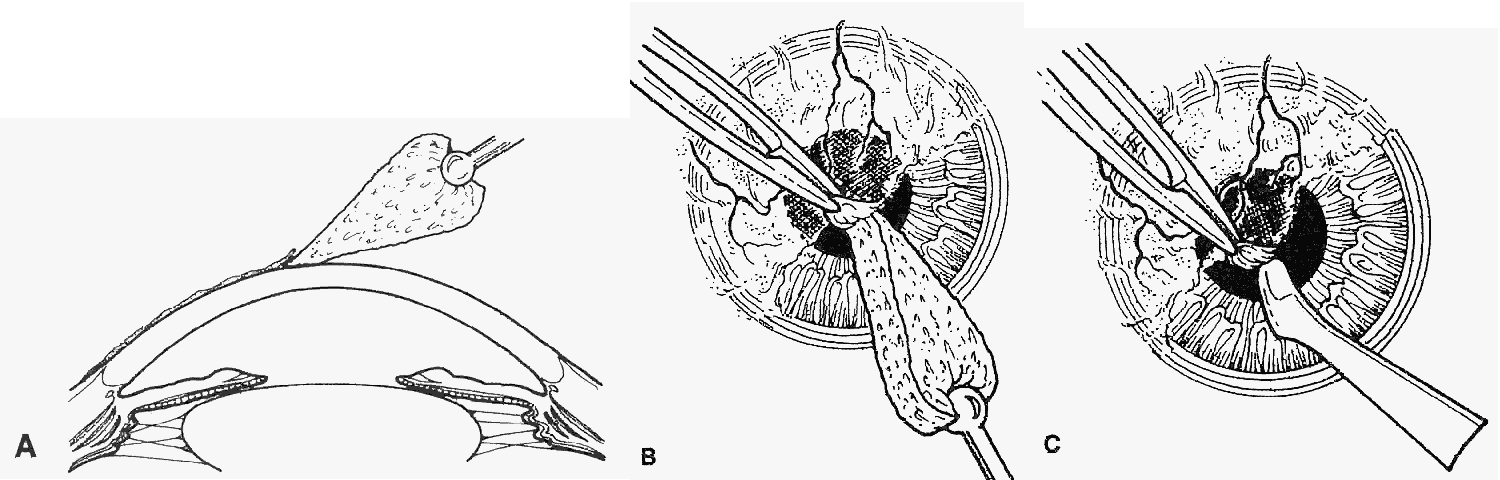
| Fig. 1. Technique of superficial keratectomy. A. A dry cellulose sponge is used to identify a cleavage plane beneath fibrovascular tissue. B. The pannus is stripped using dry sponge and tissue forceps. C. A scarifier may be used for firmly adherent tissue, remaining parallel to the cleavage plane to avoid stromal damage. (Shingleton BJ, Hersh PS, Kenyon KR [eds]: Eye Trauma. St. Louis, CV Mosby, 1991) |