
|
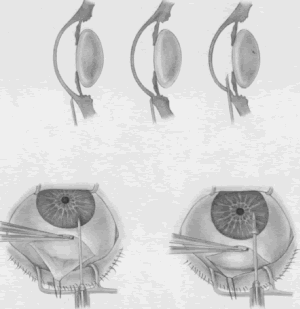
| Fig. 5. Paracentesis. It is advisable to perform a keratostomy in virtually every patient who is undergoing an intraocular glaucoma procedure. A 25-gauge, short, sharp, disposable needle is useful for this purpose and allows easy insertion of a 30-gauge blunt irrigating needle later in the procedure. To ensure that the needle does not damage the iris or lens, it must be introduced in a plane parallel to the iris. Penetration of the cornea is achieved by indentation of the cornea that is caused by pressure on the syringe, pushing the syringe and needle against the globe. Penetration is not achieved by angulating the needle. (Spaeth GL. Glaucoma surgery. In Spaeth GL (ed). Ophthalmic Surgery: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1990.) |