





|
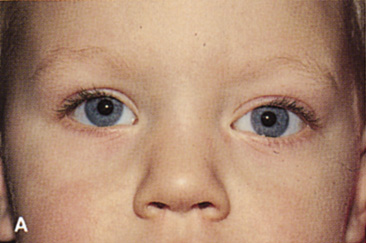
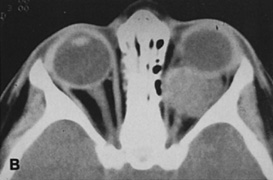
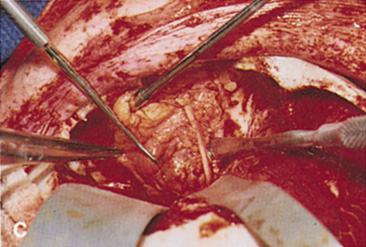
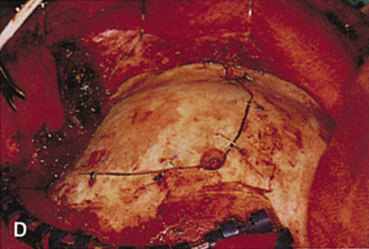
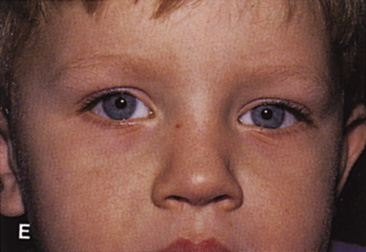
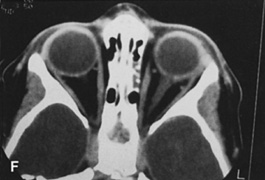
| Fig. 14. A,B. Large intraorbital lymphangioma causing proptosis and optic nerve compression in a 2-year-old child. C. View of the left orbit from above after removal of the frontal bone flap, including the supraorbital rim and orbital roof. An extensive exposure of the entire superior and lateral orbit is afforded. The levator and superior rectus complex is being retracted laterally with a muscle hook, whereas the Freer elevator retracts the superior oblique muscle medially. The frontal nerve can be seen running from posterior to anterior over the superior orbit. The orbital mass is exposed in this fashion. D. The fronto-orbital bone flap is wired back in place after completion of the procedure. E. Postoperative appearance of the patient. F. The postoperative CT scan shows complete removal of the lymphangioma. This large and diffuse lesion would have been difficult to remove with any other approach. |