
|
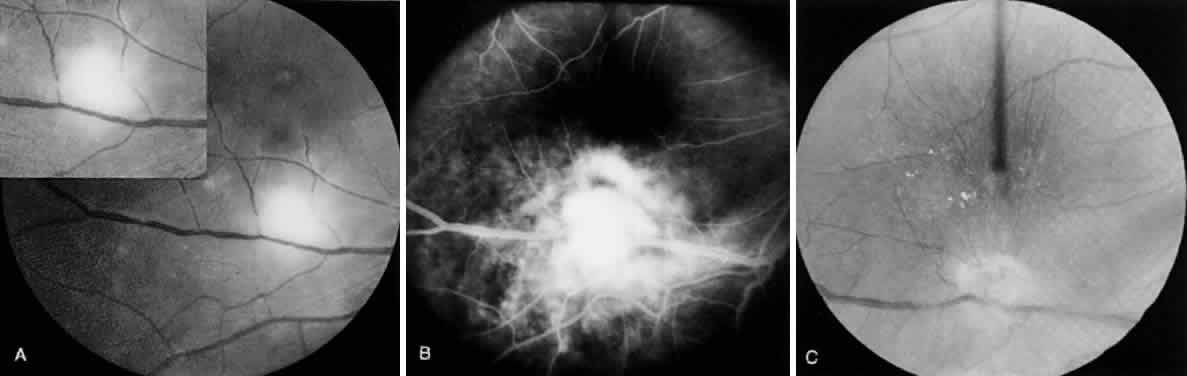
| Fig. 6. Toxoplasma retinochoroiditis after acute systemic toxoplasmosis. A 36-year-old man presented with history of seeing floaters in the right eye of 1 week's duration. The onset of his ocular symptoms occurred 56 days after a flulike illness with postauricular lymphadenopathy. Acute and convalescent serum specimens were obtained and showed an increase in Toxoplasma antibody titers from negative to 1:1024. A. Single focus of retinochoroiditis below the macular area of the right eye (vision: 20/200 [metric equivalent 6/60]). The left eye was normal with 20/20 (6/6) vision. B. Fluorescein angiography (early late phase) indicates leakage from retinal capillaries. C. Two months after a 3-week course of clindamycin, sulfadiazine, and systemic corticosteroids, the lesion completely resolved. The patient's vision decreased because of epiretinal gliotic membrane formation, causing macular pucker and subretinal neovascularization. |