
|
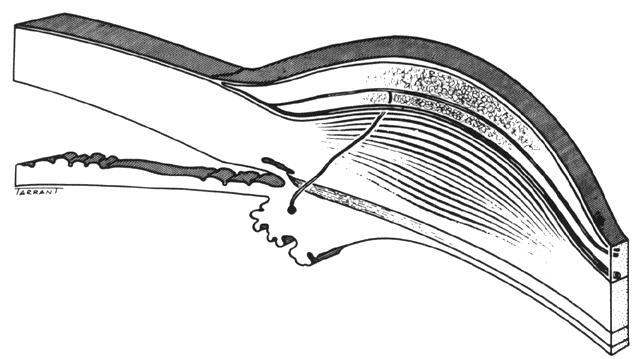
| Fig. 27. In scleritis, maximum congestion occurs in deep episcleral plexus, which is bowed forward by underlying scleral edema. Episcleral tissue is slightly infiltrated and superficial plexus is slightly congested (see Fig. 14). (Watson PG, Hayreh S, Awdry P: Episcleritis and scleritis. Br J Ophthalmol 52:278–279, 1968) |