
|
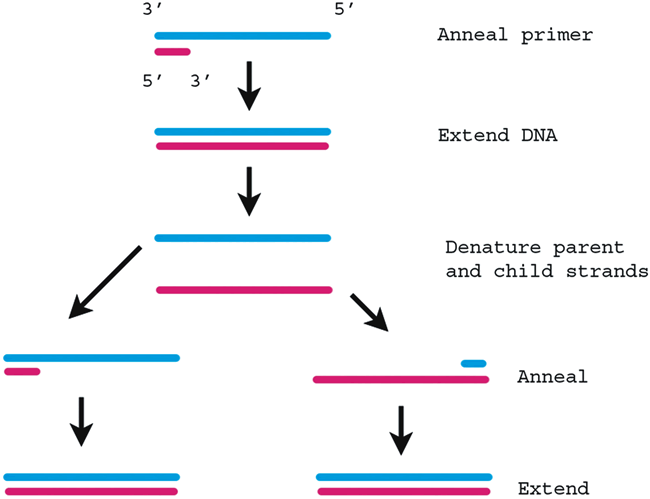
| Fig. 5. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Pathogen DNA (blue) is detected by repeated performance of PCR. An oligonucleotide primer (red) is annealed to the DNA in the sample, and extended with a thermostable DNA polymerase in the presence of appropriate buffers and nucleotide triphosphates. The parent and daughter strands are heat denatured, and oligonucleotides re-annealed. By repeated performance, exponential amplification of starting material can be achieved. |