
|
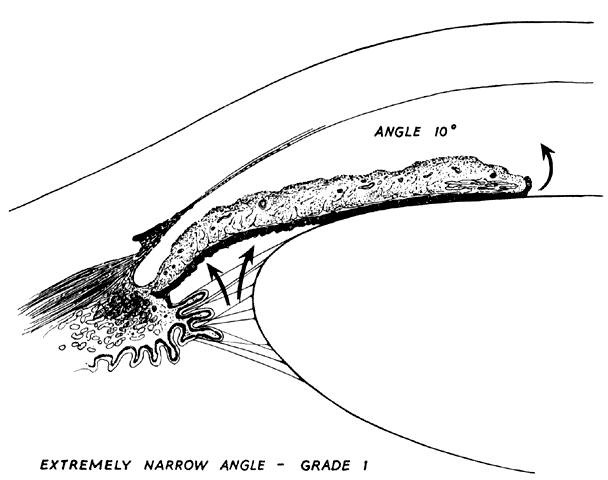
| Fig. 3. Anterior chamber angle width. Extremely narrow anterior chamber angle entrance with a mid-dilated pupil and a lax peripheral iris. Increased pressure in the posterior chamber pushes the peripheral iris forward where it lies near the filtration area; at this stage, it does not block outflow of aqueous or increase intraocular pressure. (Kolker AE, Hetherington J Jr: Becker and Shaffer's Diagnosis and Therapy of the Glaucomas, p 43. St. Louis, CV Mosby, 1970) |