
|
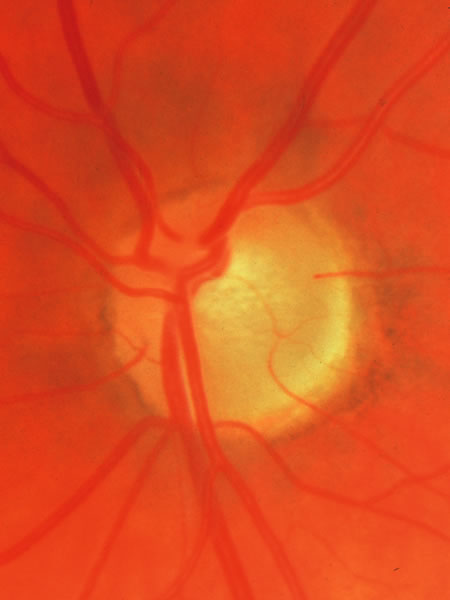
| Fig. 15. Disc without glaucomatous disease, with a tilted exit of the optic nerve. The center of the optic nerve with the vascular trunk is markedly displaced toward the upper nasal edge. The bottom of the cup is represented as a small pale area just temporal to the place where the major retinal vessels penetrate the lamina cribrosa. The lower temporal disc surface, which in a sense is the lateral and temporal wall of the cup, is a broad sloped area of neuro-retinal tissue, somewhat pale because it is spread out over the scleral support of the sloped exit canal. This is another example of a normal disc within which early glaucomatous damage in the lower temporal sector might be difficult to recognize. |