
|
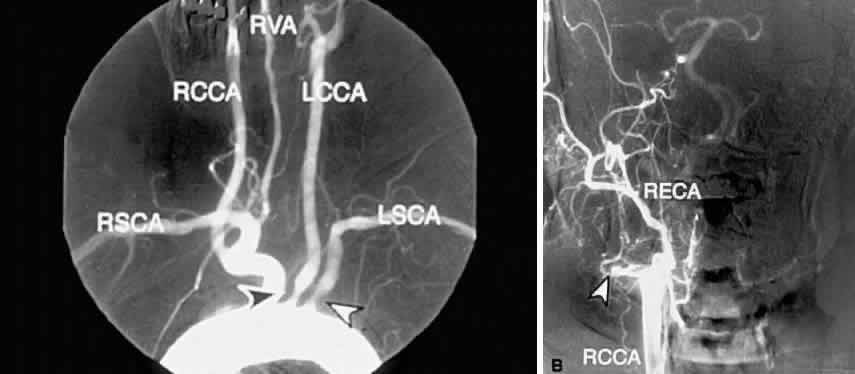
| Fig. 10. A. Digital subtraction aortogram revealing a 90% atherosclerotic stenosis of the proximal left common carotid artery (black arrowhead) and 80% stenosis of the proximal left subclavian artery (white arrowhead). RSCA, right subclavian artery; RCCA, right common carotid artery; RVA, right vertebral artery; LCCA, left common carotid artery; LSCA, left subclavian artery. B. Digital subtraction angiogram with a right common carotid injection from the same patient. There is complete occlusion of the right internal carotid artery due to atherosclerosis (white arrowhead). The right external carotid artery (RECA) and the right common carotid artery (RCCA) fill normally. |