

|
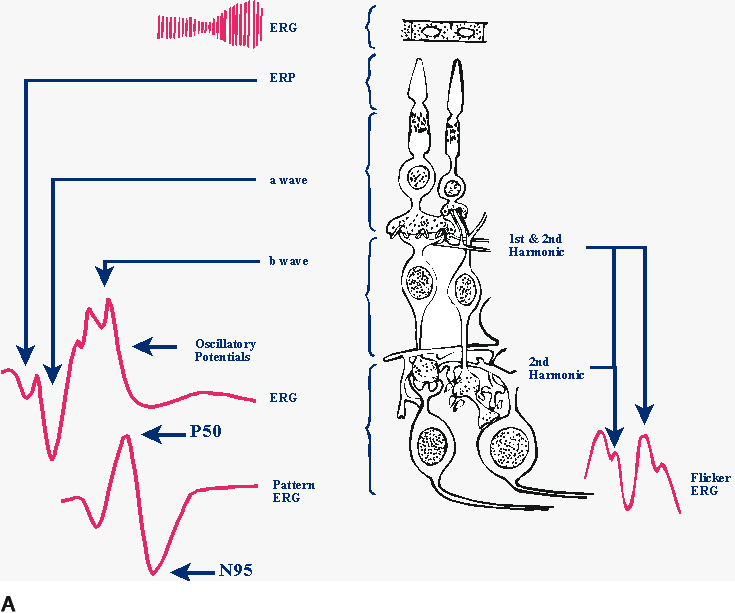
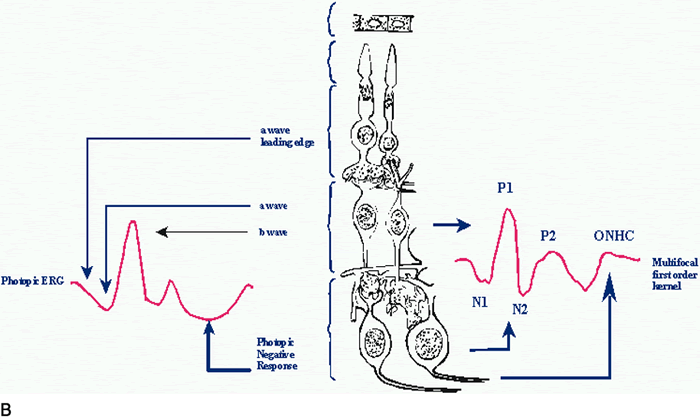
| Fig. 1. Approximate layer of origin of various retinal signals recorded from the cornea. A. On the left are a schematic dark-adapted flash-elicited electroretinogram (ERG) and a schematic pattern-elicited ERG. In the center are various retinal layers with the retinal pigment epithelium at the top and the ganglion cell layer at the bottom. On the right are the sources of 8-Hz flicker ERGs elicited by high-contrast flicker. First harmonics originate in the outer retina, whereas second harmonics have two origins: one in the outer retina and one in the inner retina. B. On the left is a schematic light-adapted flash-elicited ERG. In the center are various retinal layers with the retinal pigment epithelium at the top and the ganglion cell layer at the bottom. On the right are the sources of the multifocal ERG. The multifocal ERG appears to include sources from the middle to outer retinal layers. Different sources are emphasized, depending on the precise stimulus and recording conditions. (ERP, event-related potential; ONHC, optic nerve head component) |