
|
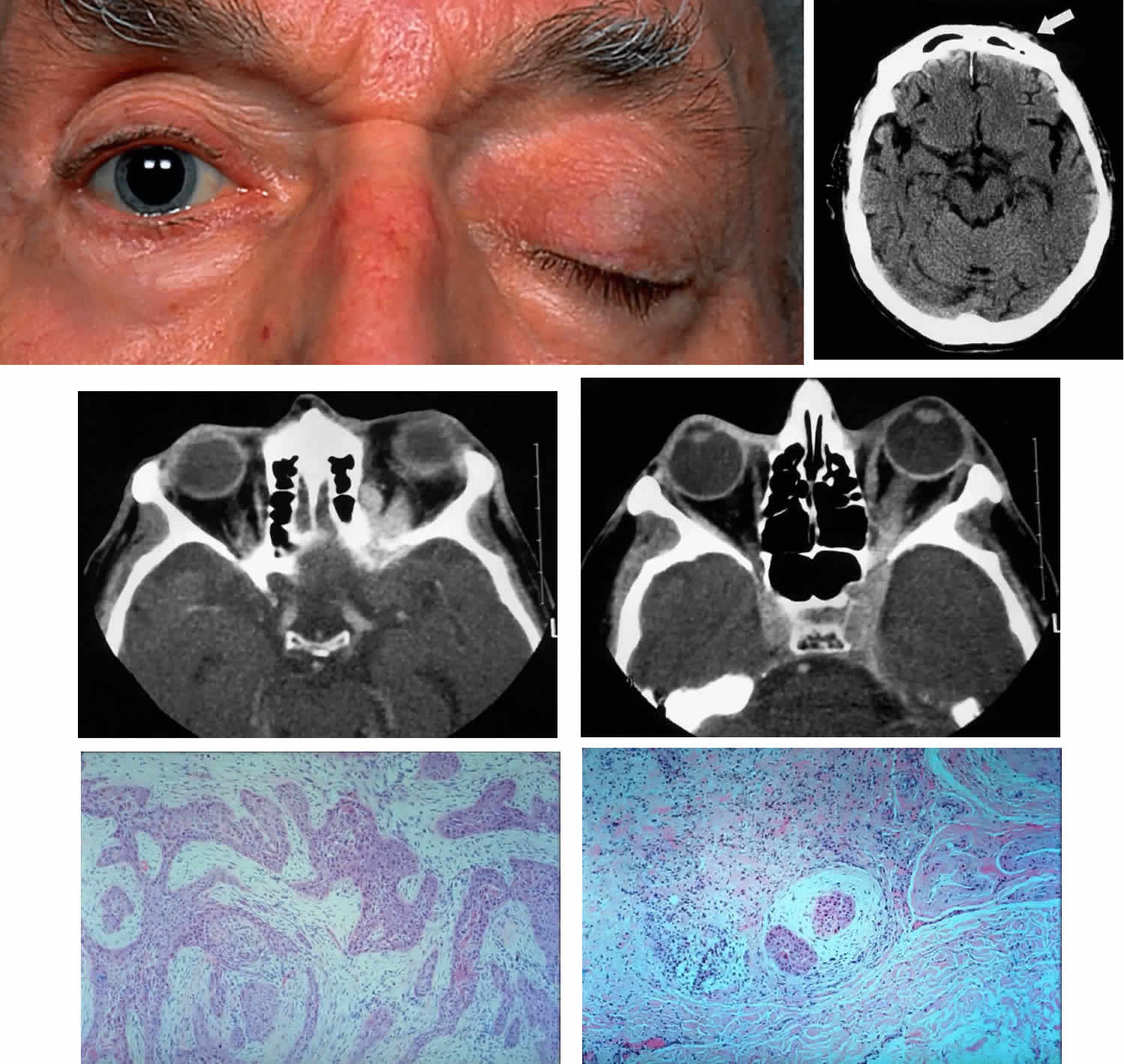
| Fig. 8. A 73-year-old man treated 3 years previously with excision of a squamous cell carcinoma in the left supraorbital region had recurrence of tumor, which was again excised. He developed progressive pain and tingling in the forehead, vertical diplopia, and finally general malaise lasting 18 months, ultimately requiring hospitalization. He was treated with corticosteroids for presumed Tolosa-Hunt syndrome, showed minimal improvement, and was discharged. Over a 2-month period, he developed decreased vision, ptosis, and bulging of the eye. On presentation he had vision of 20/80 with a relative afferent pupillary defect. There was hypesthesia in the distribution of cranial nerve V1 and hyperesthesia in V2. He had a palpable fixed cord in the forehead in the distribution of the supraorbital nerve, complete ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, and 7 mm of proptosis (A). CT scan showed local infiltration along the supraorbital nerve (B, arrow), with extension of a soft tissue mass along the orbital roof to the orbital apex (C), through a widened superior orbital fissure, and into the cavernous sinus (D). An orbital biopsy revealed cords of squamous cells (E) (H & E, × 80) and evidence of infiltration inside a small branch nerve sheath (F) (H & E, × 80). A single fraction of 10 Gy was given as palliative treatment for pain control. |