
|
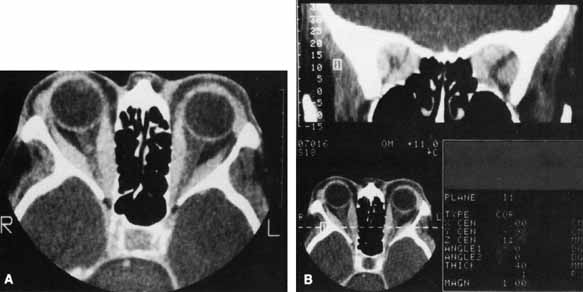
| Fig. 5 A. Axial CT scan of a patient with compressive optic neuropathy. Note that position of globe shows only mild proptosis, and orbital fat is not increased in volume. The posterior portion of the extraocular muscles is markedly enlarged, compressing the optic nerve. B. Coronal CT scan of the orbital apex in the same patient clearly shows displacement of orbital fat by enlarged muscles. The apex is “crowded,” consistent with clinical findings of optic neuropathy. |