
|
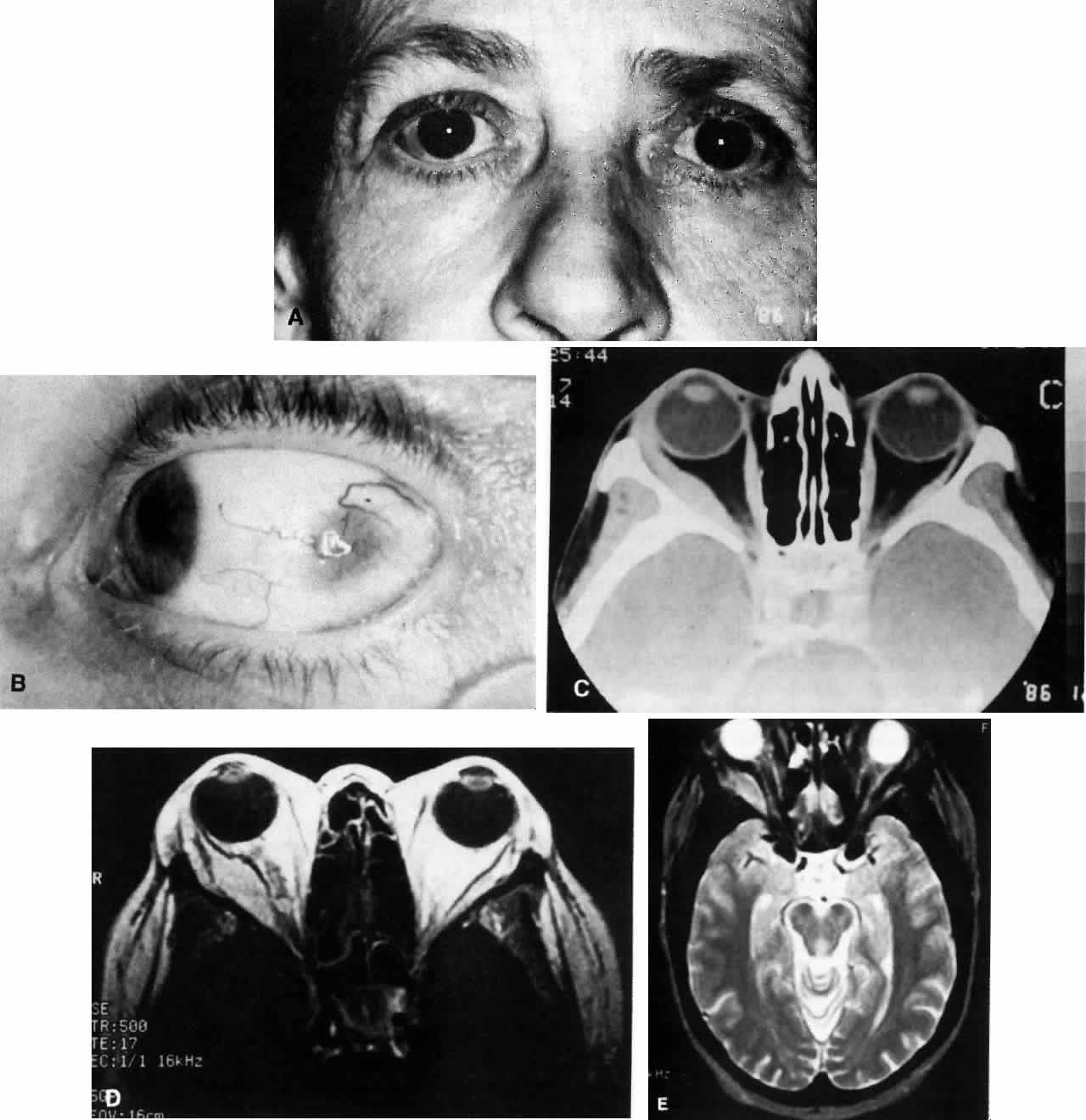
| Fig. 3. A. A 62-year-old woman presented with diplopia and minimal right-sided proptosis. B. Enlarged lateral rectus muscle is visible subconjunctivally. C. Axial CT image confirms myositis involving the lateral rectus muscle. Note that the muscle as well as its tendon are involved in the inflammatory process in contrast to muscle involvement in thyroid-related orbital disease. D. T1-weighted MRI image demonstrating myositis involving the lateral rectus muscle. In this case the muscle belly is enlarged but the tendon appears relatively unaffected. E. T2 weighted MRI image of orbital myositis showing little difference in appearance of muscle between T1- and T2-weighted images. |