
|
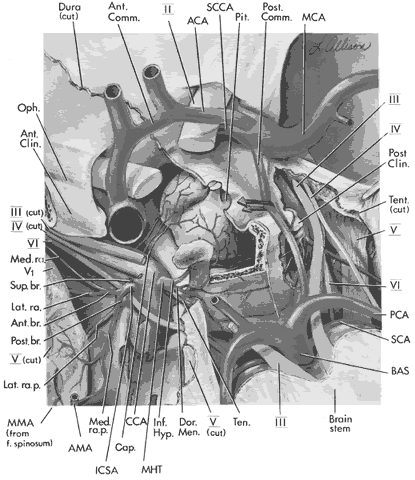
| Fig. 20. An exposed view of the cavernous sinus. The neurovascular anatomy of the cavernous sinus is shown in detail. (BAS, basilar artery; SCA, superior cerebellar artery; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; Tent. (cut), tentorium cut to demonstrate underlying arteries and nerves; Post Clin., posterior clinoid; MCA, middle cerebral artery; Post. Comm., posterior communicating artery; Pit., pituitary gland; SCCA, supraclinoid carotid artery; ACA, anterior cerebral artery; Ant. Comm., anterior communicating artery; Dura (cut), dura cut for exposure of cavernous sinus; Oph., ophthalmic artery; Ant. Clin., anterior clinoid; MMA (from f. spinosum), middle meningeal arterial branch coming from foramen spinosum; AMA, accessory meningeal artery at level of foramen ovale; ICSA, artery to the inferior cavernous sinus; Sup. br., superior branch of ICSA; Ant. br., anterior branch of ICSA; Med. ra., medial ramus of anterior branch of ICSA; Lat. ra., lateral ramus of anterior branch of medial ICSA; Post. br., posterior branch of ICSA; Med. ra p., medial ramus of posterior branch of ICSA, Cap., capsular arteries; CCA, cavernous carotid artery; MHT, meningohypophyseal trunk; Inf. Hyp., inferior hypophyseal artery of MHT; Brain stem, anterior portion of mesencephalon exposed; II, optic nerve; III (Cut), oculomotor nerve cut to allow visualization of intracavernous carotid artery and its branches; IV (cut), trochlear nerve cut; VI, abducens nerve cut; V1, first division of fifth cranial nerve ophthalmic; III, oculomotor nerve seen posteriorly and anteriorly (not cut) on reader's right; V, fifth cranial nerve seen (not cut) on reader's right. V (cut) on left. Dor. Men., dorsal meningeal artery; Ten, tentorial artery. |