
|
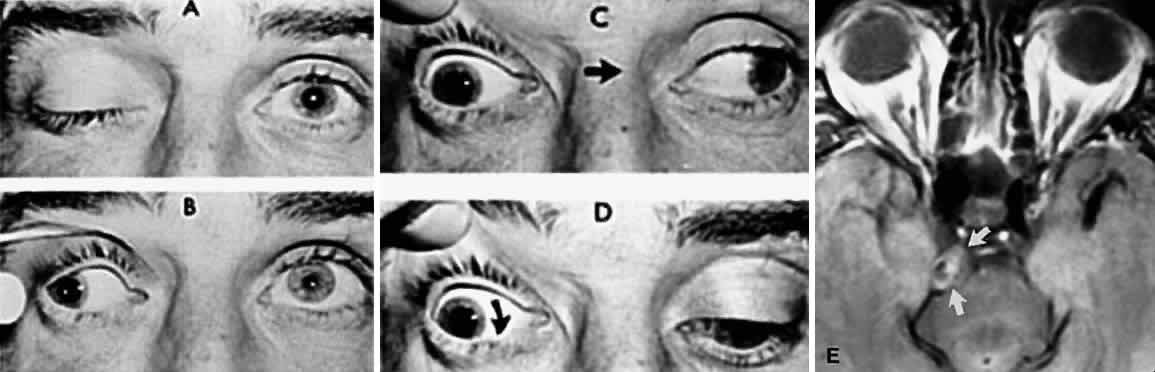
| Fig. 12. Sudden total right ophthalmoplegia accompanied by orbital pain, due to posterior communicating artery aneurysm. A. Complete right ptosis. B. Right eye in abducted position, with dilated pupil, fixed to light. C. Failure of adduction on left gaze. D. Right eye intorts (arrow) on downward gaze, indicating retained function of fourth nerve. E. Contrast-enhanced T-1 weighted MRI axial section shows aneurysm (arrows). Confirmed by angiography. |