
|
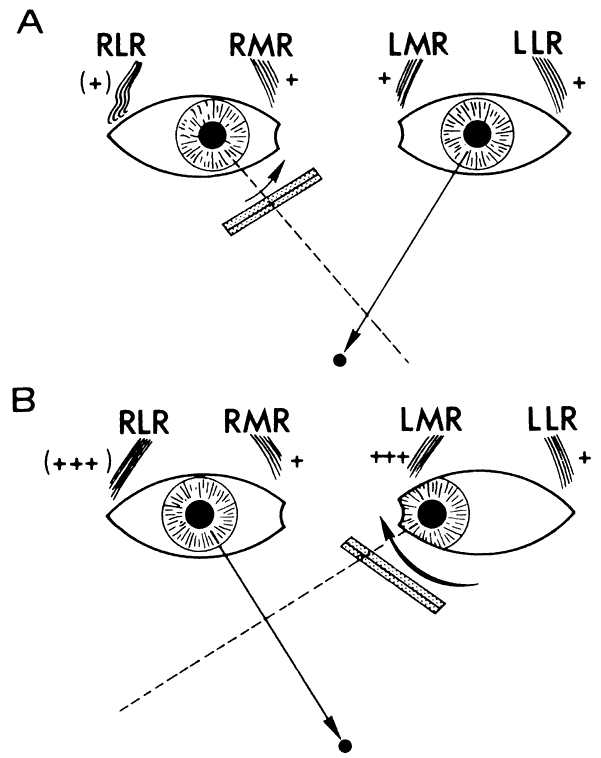
| Fig. 4. Alternate cover test used, for example, with palsy of the right lateral rectus muscle (RLR). A. With a cover over the right eye, the left (nonparetic) eye fixates and the right eye is moderately deviated inward (primary deviation). B. If the paretic right eye is forced to fixate, increased innervation (+ + + ) is delivered to both the paretic RLR and its normal yoke muscle, the left medial rectus (LMR). Subsequent overaction of the LMR markedly deviates the nonparetic eye (secondary deviation). |