
|
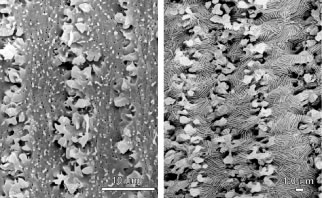
| Fig. 16. Scanning electron micrographs showing the surface morphology of (left) cortical and (right) nuclear fibers. Cortical fibers are characterized by complex lateral interdigitations arising at the angles formed by the six lateral membrane faces and arrayed along a fiber's length. In addition, small ball and socket-like interdigitations are randomly found on and within the lateral faces. In contrast, nuclear fiber lateral faces are transformed into numerous furrowed membrane domains by the reorganization of aquaporin 0s. |