
|
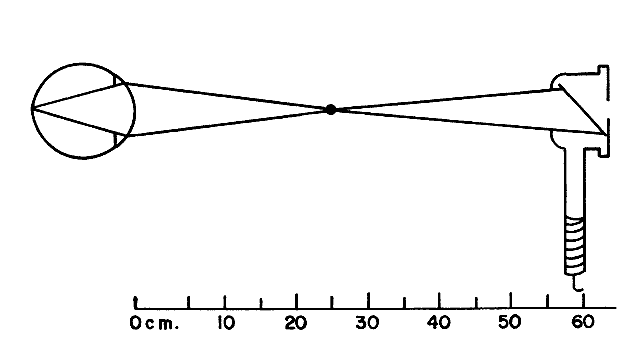
| Fig. 11. Locating the far point of a -4.00-D eye using ophthalmoscopic retinoscopy. The vergence control is adjusted (all the way up) for the maximum concave mirror effect, causing the retinoscope filament image to form about 33 cm in front of the handle. The retinoscope is placed so that the examiner sees in the patient's pupil a bright, sharply focused retinal image through the aperture. This occurs when the far point of the eye is at the same point as the image of the retinoscope. The eye shown is 4.00 D myopic and has its far point 25 cm anterior to the cornea. The far point of the eye is conjugate with the retina. (Weinstock SM, Wirtschafter JD: A Decision-Oriented Manual of Retinoscopy. Springfield, IL: Charles C Thomas, 1976.) |