
|
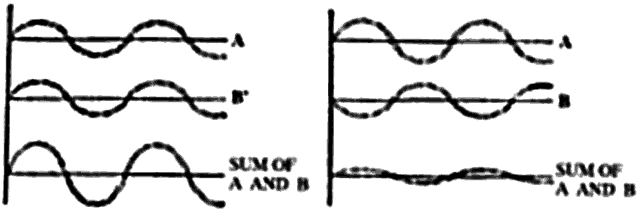
| Fig. 2. Two waves of the same wavelength constructively interfere (left) if their crests and troughs coincide, producing a resultant wave that is the summation of the two waves' amplitudes. If the crest of one wave coincides with the trough of the other, destructive interference takes place and can lead to complete cancellation (right). |